RNA Library Preparation
Advances in RNA-Seq library prep are revolutionizing the study of the transcriptome.

Whole Transcriptome
Measure gene and transcript abundance; detect known and novel features in coding and noncoding RNA. Targeted hybridization removes abundant rRNA to focus on high-value portions of the transcriptome.

mRNA
Quantify gene expression, identify known and novel isoforms in the coding transcriptome, detect gene fusions, and measure allele-specific expression.

RNA Enrichment
Analyze gene expression in a focused set of genes of interest. Provides quantitative expression information as well as the detection of small variants and gene fusions.
RNA Amplicon
Use ultra-deep sequencing of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplicons for analysis of RNA sequences of interest, differential expression analysis, allele-specific expression measurement, and gene fusion verification.

Time to Compare Custom Enrichment Workflows
Our time-lapse video shows how the entire RNA or DNA workflow can complete before your shift is done, with only 2 hours hands-on time. (DNA workflow shown.)
View Video
Introducing Enhanced RNA-Seq Library Prep Portfolio
These solutions for studying RNA for infectious disease, oncology, and genetic disease research offer rapid turn-around time, broad study flexibility and sequencing scalability.
Read ArticleChoosing an RNA Kit for Your Experiment
| Application | Product | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Total RNA Sequencing | Illumina Stranded Total RNA Prep |
|
| mRNA Sequencing | Illumina Stranded mRNA Prep |
|
| Targeted RNA Sequencing | Illumina RNA Prep with Enrichment |
|
RNA Library Prep At-a-Glance
| Application | Whole transcriptome | mRNA | RNA enrichment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hands-on time | < 3 hrs | < 3 hrs | < 2 hrs |
| Turnaround time | ~7 hrs | 6.5 hrs | < 9 hrs |
| Input | 1 to 1000 ng standard quality RNA; 10 ng for optimal performance and FFPE samples | 25 to 1000 ng standard quality RNA | 10 ng standard quality RNA; 20 ng RNA for low quality / degraded / FFPE |
| Automation capability | Liquid handling robots | Liquid handling robots | Liquid handling robots |
| PCR protocol | No | No | Yes |
| Library Quant needed? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fragmentation included? | Yes | Yes | Not required |
| Product | Illumina Stranded Total RNA Prep | Illumina Stranded mRNA Prep | Illumina RNA Prep with Enrichment |
All three kits allow you to decrease sequencing costs by loading up to 384 samples on a single NovaSeq S4 Flow Cell using 384 unique dual indexes for higher throughput sequencing.
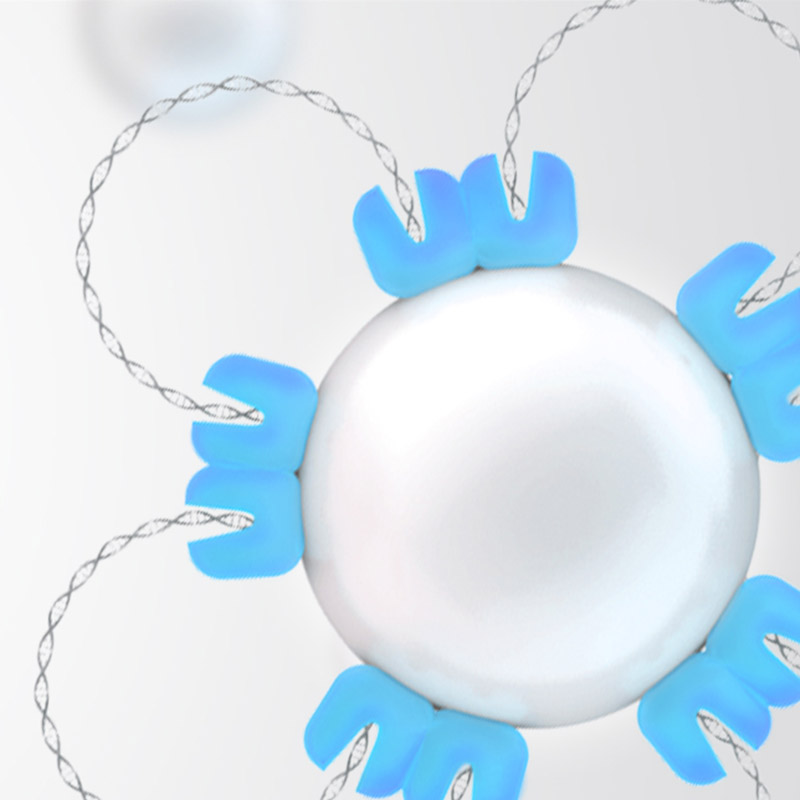
The Benefits of Tagmentation
Bead-linked transposome tagmentation is an innovative technology used in our library preparation portfolio. On-bead tagmentation lets you get to sequence-ready libraries faster than before by simultaneously fragmenting the gDNA and adding the Illumina sequencing primers. Normalize your library without ancillary reagents or equipment. Reduce turnaround time and complexity.
Learn More
Understanding Adapter Ligation
The other key technology used in our NGS library prep is adapter ligation, long known for consistent, high-quality data. Libraries are prepared by fragmenting a gDNA or cDNA sample and ligating specialized adapters to both fragment ends. These adapters contain the full complement of sequencing primer hybridization sites. This eliminates the need for additional PCR steps, making the process fully automatable.
Learn MoreFrequently Purchased Together
Ask an expert how you can get the most with Illumina Library Prep
We'll walk through your needs and make recommendations.
RNA-Seq Library Prep Methods and Use Cases
Tale of Two Kits
A critical comparison between two popular RNA Library Prep Kits reveals new information of interest to researchers conducting RNA sequencing studies.
RNA Methods Poster
A comprehensive set of NGS methods for analyzing:
- RNA transcription
- RNA–protein interactions
- Low levels of RNA
- RNA modifications
- RNA structure
RNA Methods Review
This article collection describes various NGS methods for RNA sequencing, compiled from the scientific literature including pros and cons, publication summaries, and references.
RNA Sequencing Example Workflow for Immuno-oncology Research
Library Prep
llumina RNA Prep with Enrichment
Simultaneously fragment the cDNA and add the Illumina sequencing primers.
Sequencing
NextSeq 2000
Scalable transcriptome and exome sequencing. Process up to 40 samples in a single sequencing run.
Analysis
Related Solutions
Indexing
Increase the number of samples sequenced per run and optimize high-throughput sequencing using unique dual index adapters.
UMIs
Unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) provide error correction and accuracy and can reduce false-positive variant calls while increasing variant detection sensitivity.
Automation
Our partners have developed both high- and low-throughput walk-away automation methods that span our library prep portfolio.
RNA Sequencing
Detect both known and novel features in a single assay, including transcript isoforms, gene fusions, and single nucleotide variants, all without prior knowledge.