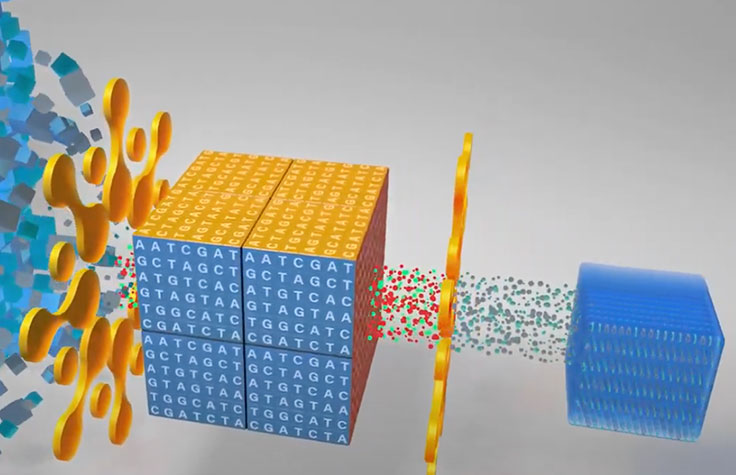
Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing
What is Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing?
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing allows researchers to comprehensively sample all genes in all organisms present in a given complex sample. The method enables microbiologists to evaluate bacterial diversity and detect the abundance of microbes in various environments. Shotgun metagenomics also provides a means to study unculturable microorganisms that are otherwise difficult or impossible to analyze.
Unlike capillary sequencing or PCR-based approaches, next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows researchers to sequence thousands of organisms in parallel. With the ability to combine many samples in a single sequencing run and obtain high sequence coverage per sample, NGS-based metagenomic sequencing can detect very low abundance members of the microbial community that may be missed or are too expensive to identify using other methods.
16S rRNA Sequencing is another method used for metagenomics studies.

Shotgun Metagenomics Methods Guide
Sequence complex microbial samples to identify emerging diseases or gain insight into microbial community biodiversity and function.
Download GuideMetagenomic Sequencing Research Articles
The Mysterious World of Microbes
Phil Hugenholtz, PhD explains how shotgun metagenomic sequencing with NGS has made a difference in his research.
Read Interview
How Microbiome Multi-Omics Can Bolster Human Health
Shotgun metagenomics methods are enabling a deeper analysis of the gut microbiome and how it contributes to, or protects from, disease.
Read Article
The Time is Now for Microbiome Studies
Whole-genome shotgun sequencing and transcriptomics provide researchers and pharmaceutical companies with data to refine drug discovery and development.
Read InterviewIDbyDNA Explify Platform Improves Results for Clinical Metagenomics Research
The Explify Platform is a fully supported NGS-based, clinical metagenomics technology suite for clinical laboratories. Watch this video for a virtual tour to understand how the Explify Platform can help your lab streamline processes, improve results, and much, much more.
Watch VideoMicrobes and Metagenomics Research Review
Metagenomics is one of the fastest-growing scientific disciplines. This document highlights peer-reviewed publications that apply Illumina sequencing technologies to metagenomics research.
Read Review
Featured Products
Suggested Workflow for Shotgun Metagenomics
There are multiple ways to perform shotgun-based metagenomic sequencing experiments, but these are some suggested products for each step of the workflow.
Click on the below to view products for each workflow step.
A fast, integrated workflow for a wide range of applications, from human whole-genome sequencing to amplicons, plasmids, and microbial species.
Nextera XT Library Prep KitPrepare sequencing-ready libraries for small genomes (bacteria, archaea, viruses), amplicons, and plasmids in less than 90 minutes.
Simple, all-inclusive library preparation for whole-genome sequencing applications. Researchers can sequence a wide variety of organisms, from small genomes such as bacteria to whole-human genomes.
Benchtop Sequencing
MiSeq SystemSpeed, accuracy and simplicity for far-reaching applications in microbiology.
NextSeq 1000 and 2000 SystemsGroundbreaking benchtop sequencers allow you to explore new discoveries across a variety of current and emerging applications, with higher efficiency and fewer restraints.
High-Throughput Sequencing
Power for shotgun metagenomics and flexibility to scale based on your project or workflow needs.
High throughput, low cost for production-scale genomics.
BaseSpace Apps for k-mer alignments and taxonomic classification
DRAGEN EnrichmentThe DRAGEN Enrichment App aligns and optionally variant calls FASTQ, BAM or CRAM files, outputting a BAM, VCF, or both.
Enables metagenomic analysis by rapidly assessing your samples from BaseSpace Sequence Hub with a fast, comprehensive, accurate data platform
Frequently Purchased Together
Metagenomics and Infectious Diseases
Infectious Disease Surveillance

NGS supports effective strategies to track infectious disease transmission. Metagenomics can help scientists identify novel pathogens and study zoonotic reservoirs to help predict and prevent outbreaks.
Learn MoreCOVID-19 Host Risk and Response
Studies of host genetic variation and immune responses may reveal COVID-19 therapeutic targets. Metagenomics can help researchers analyze microbiome differences between individuals with severe or mild COVID-19.
Learn MoreCOVID-19 Sequencing Solutions
Find solutions to detect and characterize SARS-CoV2, track transmission routes, study co-infection, and investigate viral evolution. Compare shotgun metagenomics with other pathogen NGS methods.
Learn More
Metagenomic Sequencing of Environmental Samples
Soil Microbiome Profiling

This metagenomic shotgun sequencing workflow offers fully automated soil sample preparation, sequencing, and analysis, to help researchers characterize soil microbial communities.
Read ArticleShotgun Sequencing of eDNA

Environmental DNA (eDNA) sequencing is an emerging method for biodiversity and ecosystem studies, used to analyze species that are likely abundant in a sample (such as bacteria or small eukaryotes).
Learn MoreInterested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on microbial genomics? Enter your email address.
Additional Resources

Clinical Metagenomics and COVID-19
Robert Schlaberg and Lauge Farnaes from IDbyDNA discuss applications of metagenomics to infectious diseases in the clinical realm.

Metagenomic Analysis of Environmental Samples
Shotgun metagenomic sequencing with the NextSeq 500 System provides insight into microbial responses to environmental changes in a water reservoir.

NGS to Discover New Virus Types on Skin
Illumina sequencers offer deep coverage to identify novel HPV types correlated with non-melanoma skin cancers.

Soil Metagenomics Workflow
Explore taxonomic and functional diversity of soil microbial communities with this comprehensive shotgun metagenomics workflow.

NovaSeq and Metagenomic Sequencing
Microbial metagenomic sequencing and assembly with the NovaSeq SP 2x251.
Metagenomics and Emerging Pathogens
IDbyDNA experts discuss use of metagenomics in facing the threat of emerging pathogens.
References
- Baker BJ, Sheik CS, Taylor CA, Jain S, Bhasi A, et al. (2013) Community transcriptomic assembly reveals microbes that contribute to deep-sea carbon and nitrogen cycling. ISME J 10.1038/ismej.2013.85.
- McLean JS, Lombardo MJ, Ziegler MG, Novotny M, Yee-Greenbaum J, et al. (2013) Genome of the pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis recovered from a biofilm in a hospital sink using a high-throughput single-cell genomics platform. Genome Res 23:867–77.
- Schofield MM, Sherman DM. (2013) Meta-omic characterization of prokaryotic gene clusters for natural product biosynthesis. Curr Opin Biotechnol: 10.1016/j.copbio.2013.05.001.
- Neafsey DE. (2013) Genome sequencing sheds light on emerging drug resistance in malaria parasites. Nat Genet 45:589–90.